Ever wondered if your home could slash its water bills while helping the planet? Imagine turning every rainfall into a resource that sustains gardens, flushes toilets, and even supports your drinking water supply when properly filtered. Rainwater harvesting plumbing is the key to maximizing both savings and sustainability. This expertly crafted guide reveals little-known industry secrets for every step of the rainwater harvesting journey—from initial system design to maintenance and legal tips—so you can start reaping big rewards today.

Curious How Rainwater Harvesting Plumbing Can Transform Your Water Use and Savings?
Are skyrocketing water bills or mounting concerns about water scarcity making you re-examine your resource habits? Rainwater harvesting plumbing is a smart, accessible solution that captures free rain and transforms it into a valuable household water source. This not only contributes to cost-effective water storage but also reduces your environmental footprint significantly. For example, a typical British home can collect thousands of litres annually from its roof—enough for watering gardens, flushing toilets, or washing cars, thus freeing up mains water for essential uses. By installing a tailored rainwater harvesting system —complete with efficient pipes, sturdy tanks, and innovative rain barrels—you minimize dependency on traditional water supply and boost your long-term savings.
With utility prices rising and climate unpredictability growing, understanding the ins and outs of rainwater collection sets you up for both immediate relief and future resilience. Real-life examples and expert tips will show you how the right water harvesting solutions can turn every rainfall into an economic and environmental win. Are you ready to harvest big savings with smarter plumbing?
What You Gain: Insights into Rainwater Harvesting Plumbing
- Access expert tips for rainwater harvest, system design, water storage, and maximizing efficiency
- Learn about water harvesting, harvesting tank choice, and selecting the right rainwater system
- Uncover potential cost savings, eco-benefits, and legal guidelines for rainwater harvesting
Understanding Rainwater Harvesting Plumbing: Foundations for Sustainable Water Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting plumbing forms the backbone of sustainable water management in modern homes. At its heart, a rainwater collection system channels water from your rooftop using dedicated pipes, directing it through effective filters into a suitable storage tank . The goal is to capture as much clean water as possible, reserve it safely, and then redirect it for household use. Choosing the correct size of water tank is crucial, as it must align with your roof’s surface area, local rainfall, and intended uses to optimize both water collection and savings.
A well-designed system enhances your water supply resilience, particularly during restrictions or dry seasons. By understanding the interplay between rainwater system components—such as the collection surface, first-flush diverters, and harvesting tanks—you create a reliable source of water that's cost-effective and environmentally responsible. With growing concerns over municipal water shortages, every drop harvested can count toward personal and community sustainability.
How a Rainwater Collection System Works
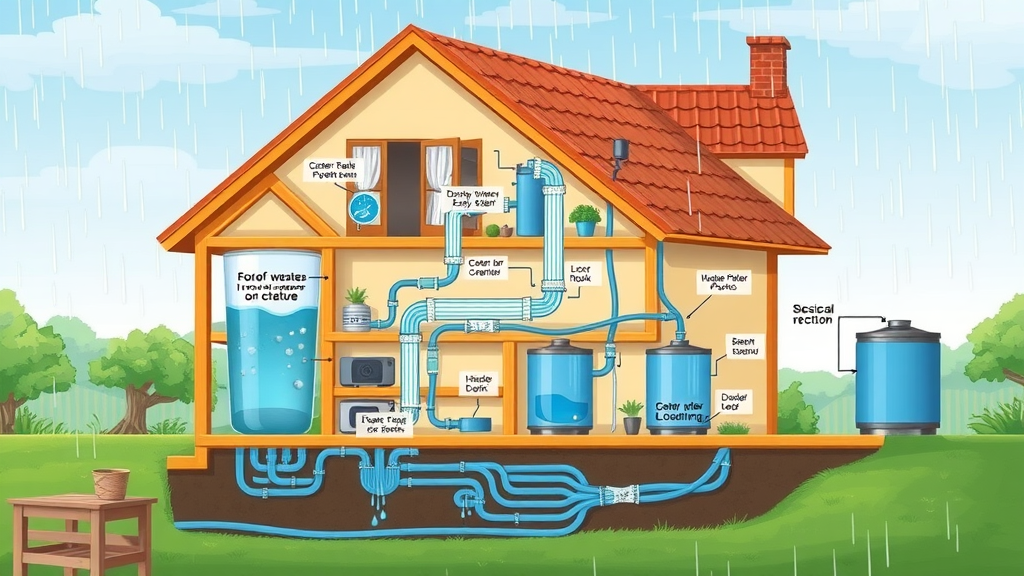
The basic operation of a rainwater collection system starts with your roof, the primary collection surface . Rainwater flows from the roof through gutters and enters a network of pipes, commonly made from safe, durable materials like PVC or polyethylene. Key points along the system include leaf screens and sediment filters, which remove debris before water reaches the tank inlet. From there, water enters storage tanks or rain barrels , where it is stored for use in irrigation, toilet flushing, and—with proper treatment—even household drinking water.
Gravity often aids water flow in these harvesting systems , but pumps and advanced control valves are sometimes added for homes with complex layouts or larger storage needs. Many rainwater harvesting setups are modular, which means they can be scaled up as your needs grow. Understanding this flow and integrating well-chosen filtration keeps your water clean, your system efficient, and ensures you’re gaining the full benefit of your rainwater harvest.
Essential Components: Harvesting System, Storage Tank, and Plumbing
A high-performing rainwater harvesting system relies on a few pivotal components working in harmony:
- Harvesting system: Includes the roof, gutters, downspouts, and filtration points, forming the backbone of the collection system .
- Storage tank: Varies in size and material but must maintain water quality and be durable enough to withstand the local climate and conditions. Consider your water storage tank a long-term investment.
- Plumbing: The pipes, connectors, and valves that transfer water from the roof to tanks, and onward to outlets like hose bibs or toilets.
Quality matters most—cheap pipes and tanks mean frequent repairs and water loss, while robust choices ensure lasting performance and safety.
Designing a Rainwater Harvesting System: From Roof to Storage Tanks
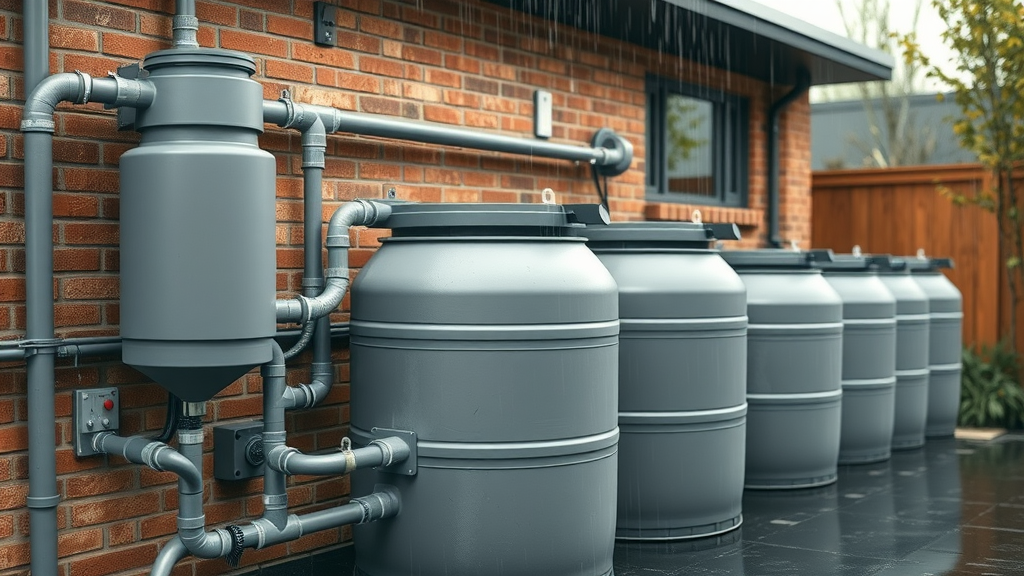

Optimizing Water Collection Using Rain Barrels, Tanks, and Piping
To capture the maximum volume of rainwater harvest , optimizing the system layout and selecting the right rain barrel , tanks, and pipes is essential. Place water tanks at or below the gutter’s lowest point for gravity-fed efficiency. Use a sufficient number of storage tanks connected via robust piping, so water is evenly distributed and accessible across the property. For garden irrigation, place rain barrels close to usage points to minimize pumping.
During heavy rain events, overflow systems (such as diverter valves or overflow pipes) protect both your tanks and home by safely channeling excess water away from sensitive foundations. Choose smooth, UV-protected pipes that prevent moss or algae growth, as this maintains the cleanliness of the harvested water and extends plumbing lifespan.
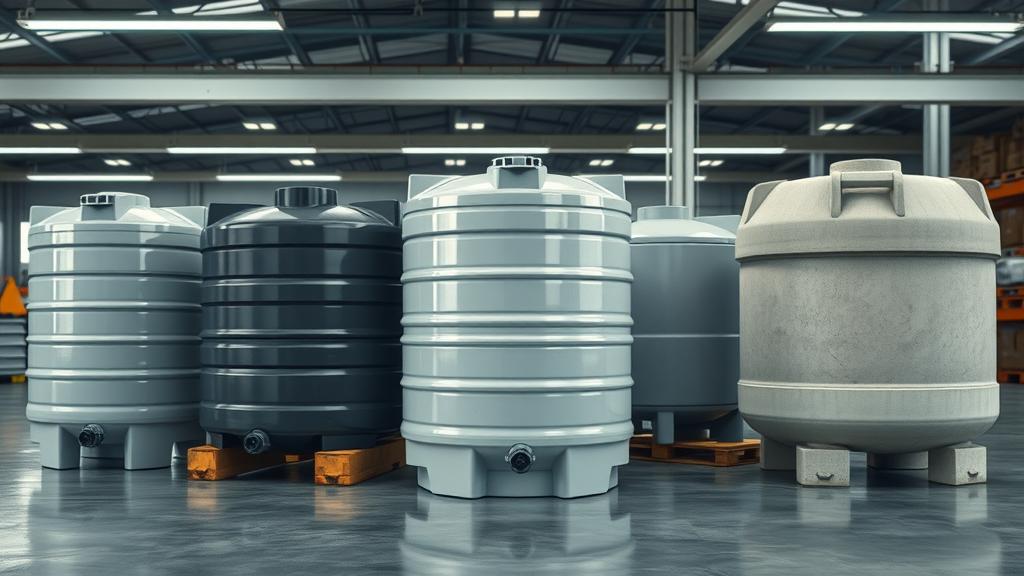
Choosing the Best Water Collection and Storage Materials
The choice of materials for your water tanks and pipes dramatically affects water purity, longevity, and cost-effectiveness. Plastic (typically polyethylene) storage tanks offer lightweight, affordable options and resist corrosion. Steel and concrete tanks, though heavier, often provide superior durability and temperature stability—ideal for larger systems. When choosing rain barrels, look for food-grade liners, especially if you plan to use water for gardens or drinking after filtration.

For plumbing, invest in pipes rated for potable water to avoid chemical leaching, and use reliable seals or connectors to guard against leaks. By selecting high-quality components at the outset, you prevent contamination and reduce maintenance in the long term. Don’t forget, the performance of your rainwater harvesting system relies as much on quality plumbing as on storage volume.
Sizing Your Rainwater Collection System and Storage Tanks: Key Calculations
Accurately sizing a rainwater collection system ensures efficiency and cost savings. Start by measuring your roof’s total square footage —the bigger the roof, the greater your potential harvest per mm of rainfall. Calculations should factor in the average annual rainfall in your region and daily household needs. Typically, one inch of rainfall over 1,000 square feet yields about 600 gallons (2,700 liters) of harvestable water.
When selecting a storage tank or multiple storage tanks , consider both the predicted collection amount and your pattern of water use (e.g., garden-only, toilet flushing, or full-home supply). Larger tanks ensure reserve during dry spells, while smaller tanks fit smaller lots but require more frequent flushing and cleaning. Only a thoughtfully sized system delivers the full savings and eco-benefits promised by rainwater harvesting plumbing.
| Tank Material | Typical Capacity (Litres) | Durability | Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (Plastic) | 200–10,000+ | 15–20 years | Low–Medium | Small to Medium Homes, Garden Use |
| Galvanized Steel | 1,000–100,000+ | 20–30 years | Medium–High | Large Homes, Commercial Use |
| Concrete | 5,000–100,000+ | 30+ years | High | Permanent Installations, High Storage Needs |
Installation Guide for Efficient Rainwater Harvesting Plumbing
Setting Up Your Water System: Key Steps
Proper installation of your rainwater harvesting plumbing sets the stage for uninterrupted savings and reliability. Begin with a well-thought-out plan that considers property slope, roof type, downspout locations, and desired water outlets. Safety and accessibility should guide the placement of tanks and pipes. It’s crucial to obtain permits as per local regulations and coordinate professional plumbing work when integrating with mains or complicated household plumbing.
Once your design is approved, foundation pads are laid for storage tanks to ensure stability and prevent shifting. Next, the collection system —gutters, downspouts, and pipes—is meticulously installed. Every joint, filter, and tank inlet is double-checked for secure, watertight connections, safeguarding water purity and minimizing losses. Attention at this stage guarantees your system’s resilience against leaks, clogs, or contamination.
- Site assessment and system design, including roof inspection.
- Choose tank locations close to primary collection points for efficient water flow.
- Prepare sturdy, level bases for tanks and rain barrels.
- Install gutters, downspouts, and diversion mechanisms.
- Fit all piping, filters, and tank inlets as per manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Connect storage tanks, test for leaks, and inspect for debris blockages.
- Integrate clean-out valves and overflow protection devices.
- Commission the complete water system, ensuring it meets local code requirements.
Connecting Tank Inlet, Pipes, and Filters in Rainwater Harvesting Plumbing
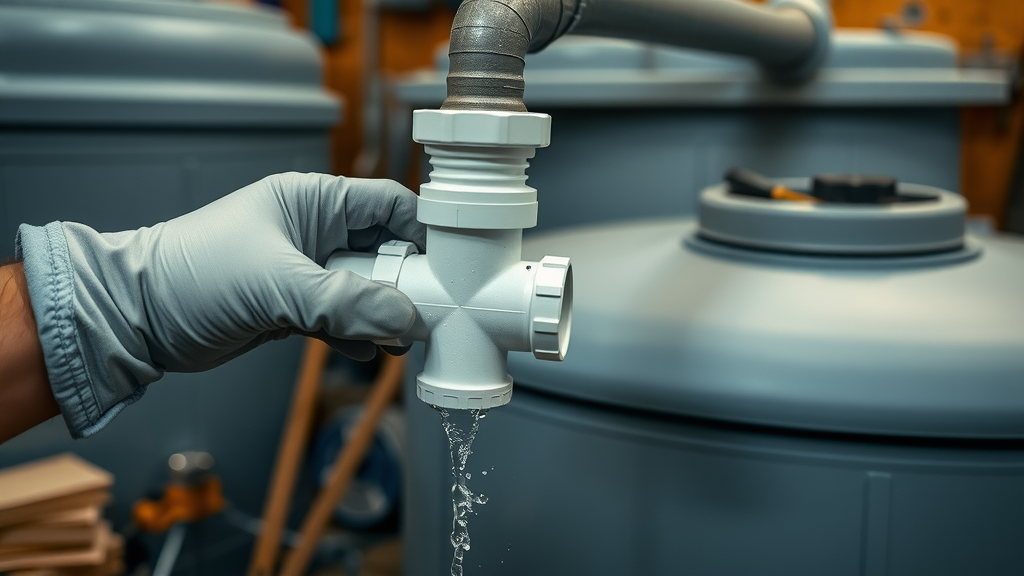

A seamless connection from collection surface to storage tank ensures your water harvesting system works efficiently with zero waste. Starting at the tank inlet , install leaf screens and sediment filters to prevent clogging and maintain high water quality. Use high-grade, UV-resistant pipes routed with gentle slopes for unimpeded flow. Joints should be robustly sealed to prevent leaks that compromise your water storage and household supply.
During this process, sediment filters or even first-flush diverters capture the dirtiest runoff, particularly at the season’s first heavy rain. It’s vital to regularly inspect these points after installation, adjusting as necessary for optimal filtering and protection of your storage tank . Well-installed plumbing isn’t just about water flow—it’s also about water purity, system longevity, and maintenance ease.
Integrating Rainwater Harvesting Systems with Existing Plumbing
Want to connect harvested rainwater for indoor use, such as flushing toilets or laundry? Rainwater harvesting systems can be integrated with your home’s existing plumbing, often through a dual-pipe setup. This involves routing rainwater supplies to non-potable water fixtures while retaining mains water for drinking. Key considerations include the use of backflow prevention devices, careful labeling, and compliance with building codes.
Upgrading an existing home may require expert help to ensure connections are safe and systems run smoothly. Retrofitting is achievable in most cases, often without invasive reconstruction, thanks to flexible piping and modular rainwater system components. Consult an experienced plumber to maximize both compliance and efficiency.
[Video: Step-by-step Installation of a Rainwater Harvesting System]
Selecting Components: Best Practices for Rainwater Harvest, Water Tanks, and Storage
How to Choose the Right Water Tanks and Rain Barrels
Selecting the right water tanks and rain barrels is foundational for a functional rainwater system. Size, material, and purpose are the three most important criteria. For garden-only watering, smaller rain barrels are suitable, while large-capacity tanks benefit whole-house non-potable supply. Look for food-grade materials if you intend to use the water for irrigation or, after filtration, for drinking water. Choose covered tanks to prevent mosquito breeding and protect from sunlight that encourages algae growth.
Ease of cleaning, outlet specifications, and structural warranties are additional factors that influence long-term satisfaction. Installing a rain barrel at each downspout, or linking multiple barrels, can provide flexibility for phased growth of your rainwater system. For large-scale harvesting, modular tanks allow for future expansion as household needs increase over time.
Selecting Efficient Pipes and Filtration Solutions for Water Harvesting

Efficient plumbing pipes and investment in top-notch filtration are critical for safe, reliable water collection . PVC and polyethylene are popular for their smooth interiors and resistance to corrosion. These materials also limit the buildup of algae and bacteria compared to older metal pipes, ensuring superior water quality and longevity.
Choose multilayered filters for the tank inlet, including mesh screens for debris and activated carbon for removing pollutants if you plan to use collected water for household tasks. Inline sediment filters between tanks and plumbing outlets further protect pumps and appliances, ensuring clear, usable water at the tap or hose.
Rainwater Collection Maintenance for Longevity and Performance

Routine maintenance keeps your rainwater harvesting system running at peak performance. To avoid algae, odors, and sediment buildup, inspect and clean gutters, filters, and tank inlets regularly—at least every season or after major storms. Remove any debris from the collection surface and rinse the filtering elements to ensure water flows freely.
For larger storage tanks, periodic draining and gentle scrubbing of internal surfaces protect the water supply from contamination. Inspect pipes for leaks, and test pumps and valves to verify operational efficiency. Long-term, this attention not only extends the lifespan of your water storage tank and rain barrels but also maintains high water quality for everyday use.
[Video: Comparing Harvesting Tank Materials for Residential Systems]
Maximizing Benefits: Water Savings, Cost Analysis, and Environmental Impact
| Home Size (sq ft) | Avg. Harvested Water/Year (litres) | Annual Mains Water Savings (£) | Reduction in Mains Water Usage (%) | Estimated Payback Period (years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,200 | 25,000 | £150 | 35% | 5–7 |
| 2,000 | 42,000 | £250 | 40% | 4–6 |
| 3,000+ | 60,000+ | £350+ | 50%+ | 3–5 |
Environmental Advantages of Rainwater Collection and Sustainable Water Supply

Implementing rainwater harvesting plumbing isn’t just about saving money—it directly supports local ecosystems and climate resilience. Every litre harvested and used onsite means less pressure on municipal water sources, aquifers, and rivers. This also reduces urban runoff and pollution, as less water flows untreated into sewers during storms.
Smaller water footprints, lower energy use for water pumping, and mitigated drought effects give your home a greener environmental profile. Rainwater collection practices, multiplied across neighborhoods, contribute to city-wide sustainability objectives and climate change adaptation.
"Adopting a rainwater harvesting system is an investment in both your household budget and a sustainable future."
Legal Considerations and Compliance for Rainwater Harvesting Plumbing
While rainwater harvesting is broadly encouraged in the UK, it must adhere to specific standards. Local councils may have rules governing tank size, placement, and overflow management. Only approved plumbing systems may connect to household supplies—especially where drinking water is concerned. Backflow prevention, labelling, and cross-connection safeguards must always be in place.
Check for any planning permissions required and inform your water authority when integrating substantial storage tanks or linking to mains supply. Professional installation ensures your system remains compliant, safe, and covered by insurance or manufacturer warranties.
Overcoming Challenges in Rainwater Harvesting Plumbing Systems
Common Problems with Harvesting Tanks, Storage Tanks, and Water Quality
Even the best rainwater harvesting systems face occasional problems. Poorly sealed tanks may admit insects or debris, while undersized or incorrectly placed tanks overflow easily and waste water. Algae, odors, and bacterial growth stem from inadequate cleaning, broken filters, or prolonged stagnation in storage tanks.
Pay heed to pipe joint integrity: leaks can develop due to age, ground movement, or careless installation. In many cases, contamination issues can be traced to the collection surface, such as uncleaned gutters or roofing materials that leach harmful chemicals into your rainwater system .
Troubleshooting Rainwater System Leaks and Maintenance
Active leaks or flow issues merit immediate attention. Routine checks—particularly after storms—help you spot escaped water or blockages before they become expensive problems. Use non-toxic pipe sealants and food-safe tank repair kits to address small cracks or leaks as they appear. If water turns discolored or develops an odor, drain, clean, and flush the system thoroughly before resuming use.
Remember, good maintenance is preventive. Thoroughly clean filters, tank inlets, and pipes before each rainy season and monitor your system’s output volume to catch efficiency drops early.
- Clear gutters and screens after each storm.
- Tighten pipe joints and check for signs of water around tank bases.
- Flush sediment from the bottom of the tank annually or as needed.
- Replace filters at manufacturer-recommended intervals.
- Keep collection surfaces free of leaves, birds' nests, or animal droppings.
[Video: How to Maintain Your Rainwater Harvesting System for Peak Performance]
People Also Ask: Answers to Common Rainwater Harvesting Plumbing Questions
What plumbing system collects rain water?
A rainwater harvesting plumbing system typically collects rainwater via roof gutters and downspouts, channeling it through pipes, filters, and into storage tanks or rain barrels. This water can then be rerouted for garden irrigation, non-potable indoor uses, or, with further treatment, as potable water supply. The key is an integrated system that safely moves and stores collected water for practical use throughout the property.
Which pipe is best for rainwater harvesting?
PVC and polyethylene pipes are most commonly recommended for rainwater harvesting due to their smooth interiors, resistance to corrosion, and ease of installation. They help maintain water quality by minimizing algae growth and withstand weather changes. Always select food-grade, UV-protected pipes if water may be used for household or drinking purposes.
What are the 10 disadvantages of rainwater harvesting?
While rainwater harvesting offers great benefits, potential downsides include: 1) Initial set-up cost, 2) Maintenance needs, 3) Risk of contamination if not maintained, 4) Space required for tanks, 5) Seasonal supply limits, 6) Structural requirements, 7) Possible mosquito breeding, 8) System complexity for large homes, 9) Legal and code compliance, and 10) Not always suitable for all roof types or climates. However, careful planning and maintenance can offset most of these disadvantages.
What is rain water in plumbing?
In plumbing terms, rainwater refers to water collected from roofs and surfaces and directed through a dedicated system of pipes, filters, and tanks, separate from your municipal mains supply. Properly managed, this water is suitable for non-potable uses or, with advanced filtration, even for drinking, making it a vital part of sustainable water management at home.
Frequently Asked Questions on Rainwater Harvesting Plumbing
- Can rainwater harvesting plumbing systems be retrofitted to older homes? Yes, most older homes can accommodate rainwater harvesting plumbing with minor adjustments, such as adding new downspouts, tanks, and dedicated piping. Consulting a specialist ensures compatibility and code-compliance for retrofits.
- How often should harvesting tanks and filters be cleaned? Clean all gutters, filters, and tanks seasonally, and inspect after major storms. Replace filter elements as the manufacturer suggests, typically every 6–12 months.
- Is harvested rainwater safe for drinking with proper filtration? With suitable, multi-stage filtration and disinfection (UV or chlorine), harvested rainwater can be safe to drink. Always test water quality regularly and follow local health guidelines.
- What are the typical costs involved in installing a rainwater harvesting plumbing system? Costs can range from £500 for simple barrel-based setups to several thousand for large, integrated storage tanks and pumps. Sizing, materials, and installation complexity all influence final price.
Key Insights for Implementing Rainwater Harvesting Plumbing Systems
- A well-designed rainwater harvesting system offers significant water savings and environmental benefits.
- Integrating the right storage tanks, pipe materials, and proper maintenance maximizes your return on investment.
Ready to Reap the Rewards of Rainwater Harvesting Plumbing?
Transform your home into a beacon of sustainability and savings! For expert help or advice from Ed Serrell Plumbing and Heating call 0796 688 4368 , or email info@edsplumbing.co.uk .
Sources
- Rain Harvesting UK – https://www.rainharvesting.co.uk
- WaterWise – https://www.waterwise.org.uk
- Environment Agency – https://www.environment-agency.gov.uk
To further enhance your understanding of rainwater harvesting plumbing, consider exploring the following resources:
-
The article “ America Should Harvest a Trillion Gallons of Rainwater ” discusses the potential of rainwater harvesting in addressing water shortages and reducing environmental impact.
-
The guide “ Rainwater Harvesting: Guidance for Homeowners ” provides detailed information on designing and maintaining rainwater harvesting systems, including considerations for plumbing and storage.
These resources offer valuable insights into the benefits and implementation of rainwater harvesting systems, helping you make informed decisions for your home.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment